Topic
Supply Chain & Logistics
Automation
Published
June 2025
Reading time
14 minutes
AI is Rewriting the Rules of Supply Chain
Unlocking a $65 billion opportunity
AI is Rewriting the Rules of Supply Chain
Download ArticleResearch
Supply chains are under pressure from multiple factors, which include rising costs, labor and material shortages, volatile demand, shifting customer expectations, geopolitical tensions, regulatory uncertainty, and mounting sustainability demands in many markets. These myriad challenges show no sign of slowing, with supply chain disruptions jumping 38% in 2024, signaling a renewed wave of instability across global networks.1 The cost of this is real: logistics inefficiencies can add up to as much as $95 billion in annual losses, impacting B2B companies the most.2
In a world of increasing global tariffs, cross-border logistics is made even more complex. Extensive tariffs on US imports, such as the 25% increase on auto imports and additional levies on countries such as China, Canada and Mexico, are compounding supply chain issues.3
Supply chains are at the core of the global economy, yet they remain one of the most labor-intensive and under-digitized functions. While automation has made some inroads, it failed to deliver on its potential. However, AI appears poised to help alleviate some of these pain points and GenAI represents the next frontier for transformative workflow improvements and operational efficiency.
Global Supply Chains Are Fragmented
Modern supply chains are increasingly complex. They’re also highly fragmented due to their cross-border nature and the fact that they operate on unstructured data. Today, over 80% of data exchanged in supply chains is unstructured.4 The problem with this is that the core operating systems—ERPs, CRMs, marketplaces—were built to handle structured data. In addition, Electronic Data Interchange (EDI) systems are outdated and inconsistently adopted. This results in fragmented communication and limited real-time visibility. Incorrect or siloed data can lead to significant financial losses, with companies potentially losing up to 30% of revenue annually.5 This is partly due to the drain on employee productivity that results from inefficiencies caused by data isolation. Despite the urgent need for innovation, logistics remains slow to evolve and 76% of digital transformations fell short of key goals, according to Gartner.6 Legacy systems and manual workflows still dominate, with nearly 50% of supply chain leaders not investing meaningfully in core digital tools like Warehouse Management Systems (WMS) or Transportation Management Systems (TMS).7
Many argue that shifting to a nearshoring or onshoring strategy is the only solution. This promises to increase gross margins by as much as 30% but comes with challenges that include high moving and capital costs, complex and time-consuming relocation projects, regulatory obstacles, and ongoing limited data visibility to manage.8 So, whilst nearshoring and onshoring may reduce supply chain fragmentation, these strategies will be difficult to successfully implement and are unlikely to offer short-term benefits.
AI solutions are well positioned to unify fragmented systems and parse unstructured data. They can successfully connect siloed sources, spot patterns, and deliver predictive insights, which together enable the end-to-end visibility needed to navigate today’s complex supply chains.
While AI won’t erase fragmentation, it is the most powerful tool yet for navigating, predicting, and optimizing within fragmented global supply chains, turning complexity into a competitive advantage for those who get it right.
Driving Efficiency Across the Value Chain
Where supply chains have historically been disjointed, AI is poised to unify disparate data sources and systems and replace cumbersome manual processes. To get a better understanding of these improvement opportunities, we have mapped out a simple value chain that captures each of the major phases within a typical supply chain.
Value Chain
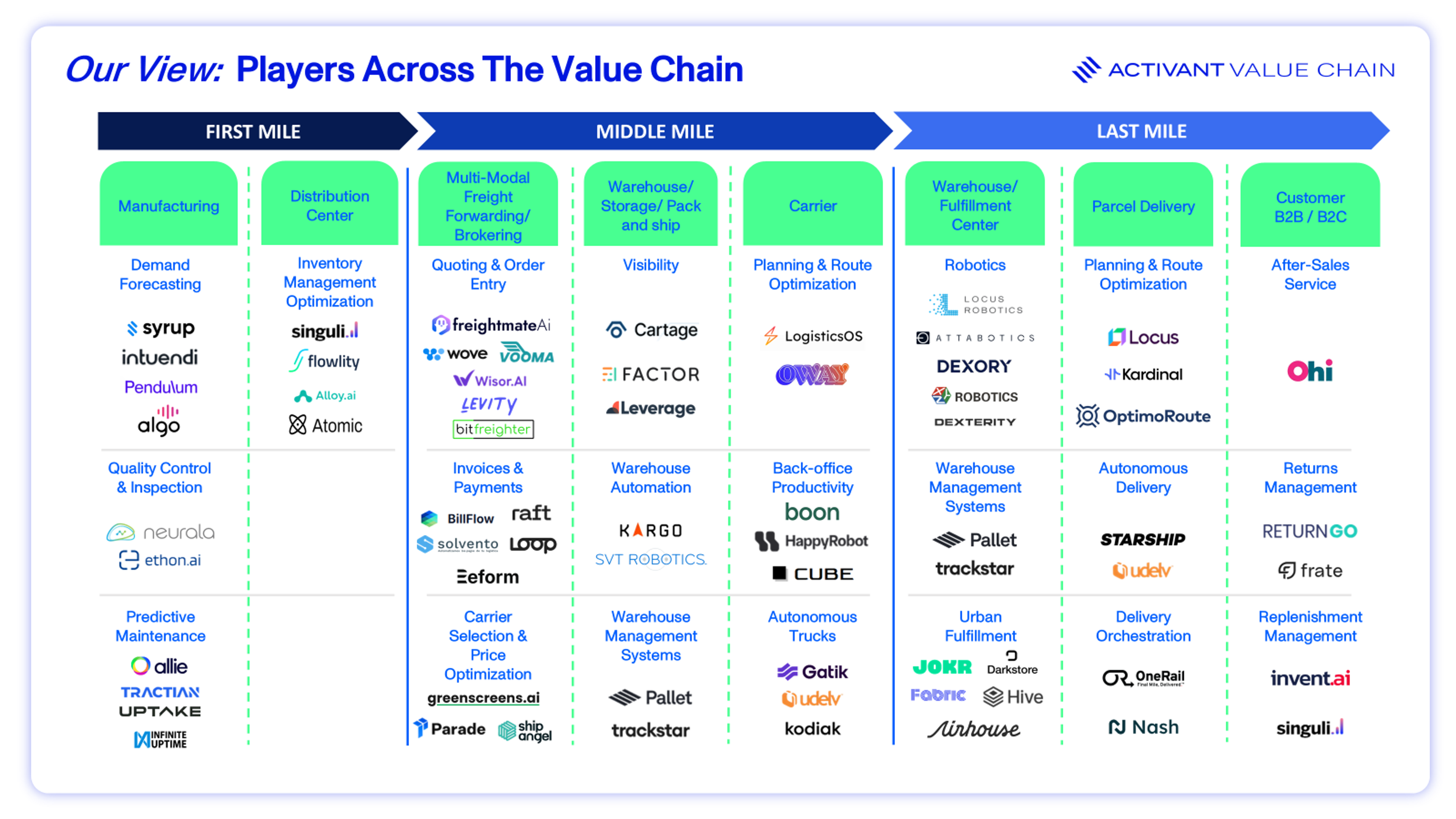
The first mile addresses the challenge of moving goods from the manufacturer or supplier to the warehouse or distribution center. It is important to get this first step right as delays, poor planning and lack of visibility ripple downstream into the rest of the supply chain. In the past, reliance on manual processes such as labelling and tracking increased the likelihood of errors and delays. Automating these tasks can enhance efficiency and reduce costs.
This segment has seen widescale adoption of AI-powered demand forecasting and inventory management tools. A recent Zero100 analysis found 16% of companies had established AI use cases in planning, from demand forecasting to replenishment and allocation.9 Companies recognize that addressing first-mile inefficiencies through AI not only reduces costs but also enhances the overall resilience and responsiveness of the supply chain.
Middle mile logistics is estimated to be worth $170 billion by 2030.10 This step is the critical link between the first and last miles, facilitating the transport of goods from warehouses to regional distribution centers. We believe that of all the value chain segments, this is currently the most under-optimized and ripe for AI-driven transformation.
It is complex and fragmented, often involving multiple vendors, third-party logistics (3PLs) and transportation modes. In the U.S., inefficiencies in middle- and last-mile logistics, particularly due to "blind handoffs" between shippers, dispatchers, 3PLs, and carriers, result in an estimated $65–$95 billion in annual waste.11 Another major middle-mile issue is empty or deadhead miles, where trucks run without cargo—affecting 36% of heavy-duty trucks in the U.S. today.12
There are various applications of AI within the middle mile, offering real efficiency gains. For example, AI-powered route optimization can lead to fuel savings ranging from 10% to 20%.13
Last mile delivery is estimated to be worth $318 billion by 2032, representing the largest segment in the value chain.14 This is the last stage of the journey which involves delivering goods from a fulfilment center or hub to the final customer. This segment accounts for between 41% and 53% of total supply chain costs.15 Urban congestion, fuel, labor, and failed deliveries drive up these costs. In fact, 10% of packages delivered in last-mile logistics need to be redelivered.16
We have already seen a reasonable amount of AI integration into the last mile delivery process, particularly by giants such as Amazon, Walmart and FedEx. The last-mile space is crowded, fast-moving, and increasingly winner-takes-most. However, we believe that there is still room for niche AI innovations that solve specific pain points like returns, failed deliveries, or carbon-optimized routing.
AI Adoption Is Moving from Experimentation to Standardization
The supply chain industry’s enthusiasm for AI is evident, with market research reports forecasting a 46% CAGR from 2022 to 2030, valuing the market at $65 billion.17 Companies are prioritizing AI adoption and Gartner reports that 70% of supply chain leaders plan to implement AI by 2025.18 In fact, top performing supply chain organizations are investing in artificial intelligence and machine learning (AI/ML) to optimize their processes at more than twice the rate of low performing peers.19
Core segments of the supply chain may be technologically underserved, but we see an opportunity for AI to add real value in five specific areas. These fall across all sections of the value chain and are represented by the shaded areas in the exhibit below.
Value Chain

Below we will touch on each of these areas, and take a closer look at the efficiencies that AI is helping to generate:
Predictive Analytics: Enhancing Forecasting and Decision Making
We touched on this in our piece on the future of demand forecasting software.20 Here we highlighted how dead stock can cost businesses as much as 11% of revenue.21 Organizations that are early adopters of AI achieved a 35% decrease in inventory levels through AI-driven tools.22 This means companies are holding less stock, which frees up capital, reduces storage costs, and minimizes the risk of obsolescence. In terms of segment adoption, demand forecasting tools have emerged as a leader, accounting for 35.3% of market share in 2024.23
Warehouse Automation and Robotics: Streamlining Fulfilment Centers
The use of AI in warehouse management systems has surged, with 70% of large-scale warehouses adopting AI-driven solutions by 2024.24 AI is transforming warehouse automation by enabling smarter, faster, and more efficient operations. It powers robots that can pick, pack, and sort items, while optimizing storage layouts in real time. This reduces human error and speeds up fulfillment. By combining automation with intelligent decision-making, AI helps warehouses boost productivity and adapt to changing demand.
AI-enhanced Supply Chain Visibility: Real-time Tracking and Transparency
Around 68% of supply chain companies have adopted AI-powered traceability and visibility tools that help to enhance transparency.25 AI is revolutionizing supply chain visibility by unifying data across systems and providing real-time insights into inventory, shipments, and potential disruptions. It can track goods in motion, detect anomalies, and forecast risks before they impact operations.
Logistics and Transportation
AI is driving major advancements in logistics and transportation by optimizing routes, predicting delivery times, and improving fleet management. Implementing AI-driven route optimization can lead to significant cost reductions, including a 22% decrease in transportation expenses.26 AI also powers autonomous vehicles, dynamic scheduling, and predictive maintenance—making logistics networks faster, smarter, and more cost-efficient.
The proof of the pudding is in the eating: successfully implementing AI-enabled supply-chain management has enabled early adopters to improve logistics costs by 15%, inventory levels by 35%, and service levels by 65%, compared with slower-moving competitors.27
Procurement and Supplier Selection
Approximately 75% of supply chain professionals utilized AI-driven data analytics for smarter decision-making in 2024.28 AI is reshaping procurement by analyzing supplier data to optimize selection based on cost, reliability, and risk. It helps teams make faster, smarter decisions, automates sourcing tasks, and flags potential disruptions—boosting both efficiency and resilience. We have already covered this segment in depth in our pieces on supplier intelligence and AI in procurement.29,30
Challenges to Address
As AI tools become more accessible, sourcing the right services becomes paramount to meet an organization’s needs for success. While AI is growing and is the future of supply chain, there are still inherent challenges that need to be addressed and mitigated:
- Data Integrity: While GenAI is improving its ability to handle unstructured data, its accuracy still depends on data quality. Effective forecasting and decision-making with AI begin with clean, reliable data.
- Legacy Systems and Static Infrastructure: Outdated technologies pose a major barrier to AI integration in supply chain management. Legacy systems, often deeply embedded in operations, are costly and slow to modernize, resulting in inefficiencies and limiting adaptability. Once innovative, these systems now fall short of meeting today’s fast-changing market demands.
- Security: AI systems are susceptible to cyberattacks that can expose sensitive supply chain data and disrupt operations. These risks highlight the need for ongoing monitoring, strong security protocols, and regular vulnerability assessments.
- Cost: AI projects are often underestimated, leading to unexpected costs and setbacks. Key cost drivers include whether companies build custom models or buy off-the-shelf solutions, each with distinct budget implications. Beyond development, maintaining AI infrastructure can be resource intensive. These systems rely on networks of processors that require regular upkeep and, over time, energy demands and utility costs can rise sharply, increasing operational overheads.
- Securing And Retaining the Right Talent: AI success depends on experts customizing solutions to a supply chain’s unique needs—a complex, essential task requiring time, investment, and close collaboration with AI providers to ensure effective integration.
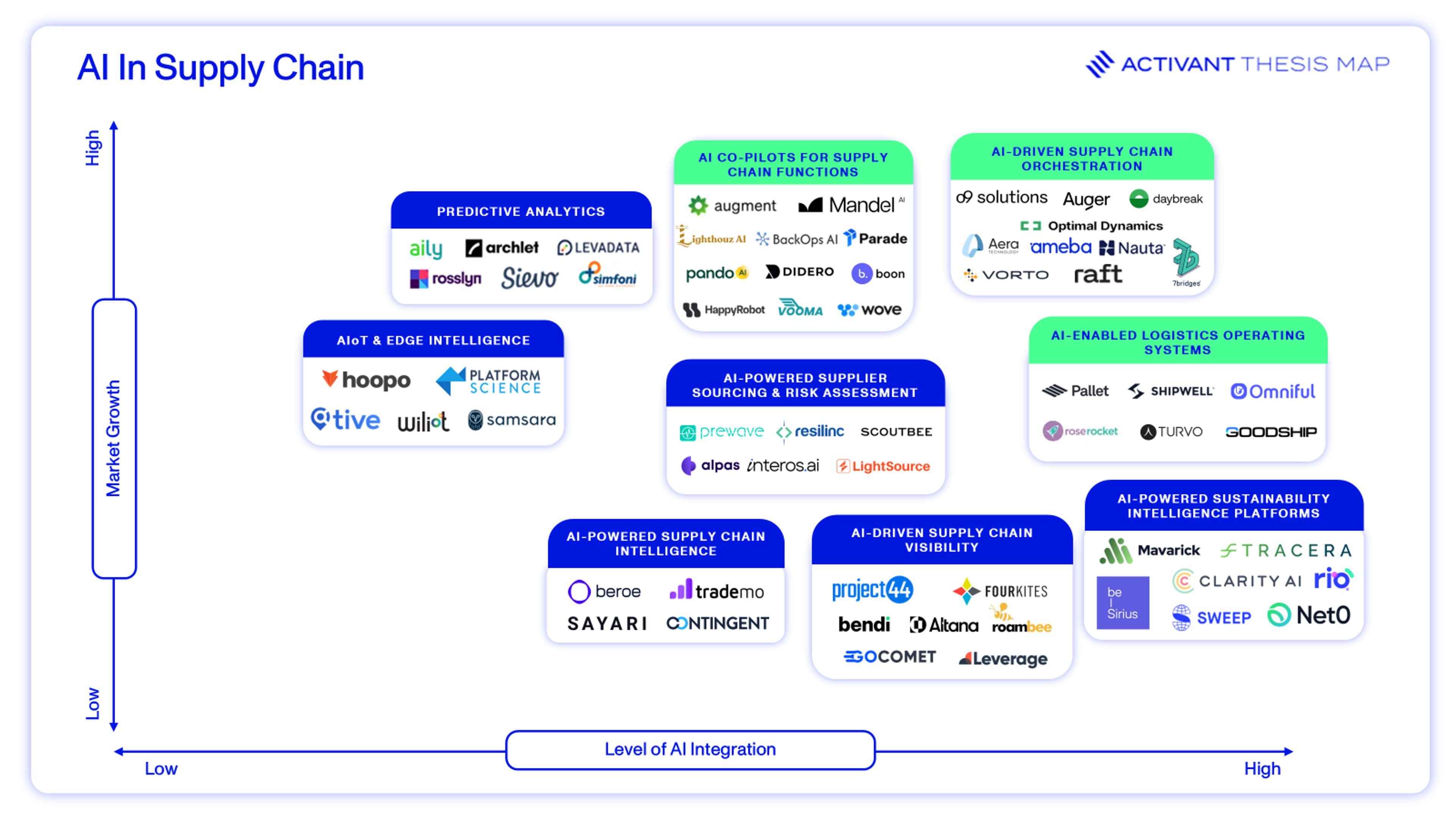
Mapping The Landscape
When creating our market map, we decided to do things a little differently. Rather than assessing players according to the categories created in our value chain, we took an AI lens when mapping the landscape. As we assessed each company, we created a framework that focused on (1) the level of AI integration (x-axis) and (2) the predicted market growth (y-axis). Note that the level of AI integration reflects whether AI is merely analyzing outputs or actively driving decisions across various supply chain functions.
We are most excited about the opportunities within AI-driven supply chain orchestration, AI-enabled logistics operating systems and AI co-pilots for supply chain functions but there are naturally opportunities across the market.
Thesis Map

AI Orchestrators: These are platforms or systems that coordinate complex supply chain activities by connecting data, systems, and decision-making processes using artificial intelligence. We see these solutions as a central AI "brain." According to Gartner, 68% of companies report poor returns on digital investments—often due to a lack of integration and coordination.31 We believe orchestration platforms help solve this by connecting systems, streamlining workflows, and enabling real-time decision-making. As a result, we expect to see increased adoption of end-to-end orchestration models to break down silos.
Auger is building an end-to-end AI-powered operating system that unifies data for seamless, real-time insights and powerful automation. Raft is an AI-powered logistics platform that automates workflows across the entire freight forwarding lifecycle, including operations, finance, and customs. The Raft AI models have been trained on five billion labelled logistics documents and data points so far. We are also excited about Optimal Dynamics, whose decision automation platform, CORE.ai, integrates strategic planning, tactical operations, and real-time dispatch to enhance efficiency and profitability for truckload carriers.
AI-powered Logistics Operating Systems: These are commonly known as Transportation Management Systems (TMSs), software platforms that optimize the planning, execution, and monitoring of freight and transportation operations. These systems use AI to help automate tasks like route planning, carrier selection, load consolidation, and exception management using real-time data and predictive analytics. Our research piece on the future of transportation managements systems touches on this further.32
Pallet, an Activant portfolio company, is an AI-powered logistics platform offering a unified TMS and Warehouse Management System (WMS) to streamline supply chain operations. Its AI assistant, CoPallet, automates tasks like tracking, quoting, and billing while integrating warehousing and transportation workflows. Rose Rocket’s platform, TMS.AI, includes features such as: Rosie, an AI assistant that streamlines order processing; DataBot, which extracts and inputs data from text and images; and a Freight Audit & Pay tool that automates invoice matching. The platform is trusted by over 100,000 users daily.
Each year, $1 Trillion is lost to manual logistics tasks like data entry, carrier coordination and lane quoting. We're building to automate the entire stack and unlock real supply chain productivity. Pallet is the operating system for a new era of logistics."

Sushanth Raman, Founder & CEO, Pallet
AI Co-pilots: This refers to solutions that enhance human decision-making in the supply chain by providing predictive insights, risk mitigation, and scenario analysis. LLM-powered assistants are embedded within procurement, logistics, and planning tools, and are thus able to augment both strategic decisions and day-to-day operations.
Augment offers Augie, an AI teammate for shippers, brokers and carriers that calls, emails, logs into systems, collaborates, escalates and does anything in between to complete a complex task. Augie claims to not just help operators work smarter, but to make logistics better. We’re also interested in Mandel, which has created an AI procurement agent. Founded in 2023 and part of Y Combinator's S23 batch, Mandel AI has processed over $50 million in material spend and managed more than 40,000 email threads.
Supply chain AI is evolving beyond simple decision support into process orchestration. The key insight we've gained is that certain workflows, like qualifying and negotiating with carriers for loads, can be fully automated while still maintaining quality and compliance. This approach eliminates the noise—where typically two-thirds of carrier conversations don't progress—and creates space for freight professionals to focus on strategic work that truly needs human creativity and judgment."

Anthony Sutardja, Co-Founder and CEO, Parade
Outside of these three segments, we see many exciting companies:
a. LightSource is an AI-native sourcing platform that automates the procurement process from RFQ to award, enhancing efficiency and collaboration between buyers and suppliers. The platform has processed over $1 billion in spend.
b. Prewave is an AI-powered supply chain risk management platform that monitors supplier networks across over 200 risk categories and in more than 400 languages, providing real-time alerts on ESG, compliance, and operational risks.
c. Sievo helps large enterprises turn complex spend data into actionable insights. Its platform uses AI and machine learning to unify, cleanse, and analyze procurement data across systems, enabling better supplier management, cost savings, risk reduction, and ESG tracking.
d. Trademo uses AI to provide visibility into international trade flows, supplier networks, and compliance risks.
e. Altana is an AI-powered platform that provides dynamic, multi-tier visibility into global supply chains, enabling businesses and governments to manage compliance, sustainability, and risk.
f. Leverage offers tools for purchase order automation, shipment tracking, and supplier performance management, integrating seamlessly with major ERP systems like SAP, Oracle, and NetSuite.
g. Mavarick’s AI-driven platform automates Scope 3 data collection, validation, reporting and analysis so enterprises with complex supply chains can focus on sustainability, not admin.
h. Tracera offers an AI-powered platform that automates the collection, verification and auditing of sustainability data with finance-grade accuracy and traceability. Its solution reduces the time and cost of sustainability data management by up to 85%.
i. Platform Science, an Activant portfolio company, provides a connected vehicle platform for commercial fleets. Its technology enables fleets to develop, deploy, and manage mobile devices and applications directly on their vehicles, streamlining operations and enhancing driver productivity.
j. Wiliot develops battery-free IoT tags called IoT Pixels, which track products in real time using ambient energy. Its cloud platform uses AI to turn this data into insights for improving supply chain efficiency and sustainability.
The Big Picture
AI is reshaping logistics by improving efficiency, visibility, and automation across freight, warehousing, and transportation. Its ability to process vast amounts of data and enhance decision-making makes it a game changer—but unlocking its full value requires organizational change, not just technology. AI-native startups have a $65 billion opportunity to transform logistics from a traditionally rigid industry into an adaptive, responsive system. The most impactful solutions go beyond single-use cases, enabling end-to-end AI integration with minimal human intervention.
We would like to hear from you if our work resonates or if you have a different perspective.
Endnotes
[1] Resilinc, The Top 5 Supply Chain Disruptions of 2024, 2025
[2] McKinsey & Company, Digitizing mid-and last-mile logistics handovers to reduce waste, 2024
[3] Reuters, Trump tariff liberation means endless complication, 2025
[4] BEM, The hidden cost of unstructured data in supply chain, 2024
[5] SCX, The Hidden Costs of Data Silos in Supply Chain Planning, 2023
[6] Gartner, Press Release, 2024
[7] McKinsey & Company, Operational efficiency: A clear path to outperformance in distribution, 2023
[8] Bain & Company, Nearshoring: Overcoming the Obstacles, 2025
[9] Zero100, A New Framework For a New Era: The Loop, 2024
[10] Lotte Global Logistics, Middle Mile Logistics: Overcoming Common Challenges, 2025
[11] McKinsey & Company, Digitizing mid- and last-mile logistics handovers to reduce waste, 2024
[12] TRUCKNET, Empty Miles – Problems And Solutions, 2021
[13] Elite Extra, AI in Logistics: Driving Efficiency and Cost Savings, 2023
[14] GlobeNewswire, Last Mile Delivery Set to Grow at a Remarkable Reach, 2024
[15] Routific, Last Mile Delivery Costs – Challenges and Solutions, 2023
[16] McKinsey & Company, Digitizing mid- and last-mile logistics handovers to reduce waste, 2024
[17] DAIMAGISTER, The AI Revolution in Logistics: a $64 Billion Opportunity, 2024
[18] Proxima, 5 Key Areas Where AI In Supply Chain Can Positively Impact An Organization, 2024
[19] Gartner, Top Supply Chain Organizations are Using AI to Optimize Processes at More Than Twice the Rate of Low Performing Peers, 2024
[20] Activant Research, The Future of Demand Forecasting Software, 2024
[21] Katana, The dead stock survival guide for manufacturers, 2025
[22] Artsmart AI, AI in Supply Chain, 2024
[23] Ibid.
[24] Meteor space, Important warehouse automation statistics you can’t ignore, 2025
[25] Artsmart AI, AI in Supply Chain, 2024
[26] RTS Labs, Transforming Logistics with AI: Boost Efficiency and Cut Costs, 2024
[27] McKinsey & Company, Succeeding in the AI supply-chain revolution, 2021
[28] Ibid.
[29] Activant Research, Supplier Intelligence, 2024
[30] Activant Research, AI in Procurement, 2025
[31] Tech Monitor, Survey shows digital initiatives failing to meet targets for 52% of enterprises, 2024
[32] Activant Research, The Future of Transportation Management Systems, 2023
The information contained herein is provided for informational purposes only and should not be construed as investment advice. The opinions, views, forecasts, performance, estimates, etc. expressed herein are subject to change without notice. Certain statements contained herein reflect the subjective views and opinions of Activant. Past performance is not indicative of future results. No representation is made that any investment will or is likely to achieve its objectives. All investments involve risk and may result in loss. This newsletter does not constitute an offer to sell or a solicitation of an offer to buy any security. Activant does not provide tax or legal advice and you are encouraged to seek the advice of a tax or legal professional regarding your individual circumstances.
This content may not under any circumstances be relied upon when making a decision to invest in any fund or investment, including those managed by Activant. Certain information contained in here has been obtained from third-party sources, including from portfolio companies of funds managed by Activant. While taken from sources believed to be reliable, Activant has not independently verified such information and makes no representations about the current or enduring accuracy of the information or its appropriateness for a given situation.
Activant does not solicit or make its services available to the public. The content provided herein may include information regarding past and/or present portfolio companies or investments managed by Activant, its affiliates and/or personnel. References to specific companies are for illustrative purposes only and do not necessarily reflect Activant investments. It should not be assumed that investments made in the future will have similar characteristics. Please see “full list of investments” at https://activantcapital.com/companies/ for a full list of investments. Any portfolio companies discussed herein should not be assumed to have been profitable. Certain information herein constitutes “forward-looking statements.” All forward-looking statements represent only the intent and belief of Activant as of the date such statements were made. None of Activant or any of its affiliates (i) assumes any responsibility for the accuracy and completeness of any forward-looking statements or (ii) undertakes any obligation to disseminate any updates or revisions to any forward-looking statement contained herein to reflect any change in their expectation with regard thereto or any change in events, conditions or circumstances on which any such statement is based. Due to various risks and uncertainties, actual events or results may differ materially from those reflected or contemplated in such forward-looking statements.







